
- #CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION HOW TO#
- #CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION CODE#
- #CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION FREE#
Mean is the mean value of the sample data. N is number of observations(sample size). They are described below.įollowing is the description of the parameters used in above functions − Normal distribution (Gaussian distribution) is a probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean. R has four in built functions to generate normal distribution. The table utilizes the symmetry of the normal distribution, so what in fact is given is ( P0 le x le a ) where a is the value of interest. If X hasa&normal&distribution&with&mean& µand&standard& deviation&, then isdistributed&standard&normal. 7 The&Standard&Normal&Distribution The&standard&normal&distribution&rarely occurs.

This can be used to compute the cumulative distribution function values for the standard normal distribution. We&use&special¬ation&to&denote&the&cdf&of&the&standard& normal&curve: (z) Z z 1 f (y 0, 1) dy. This is referred as normal distribution in statistics. The table below contains the area under the standard normal curve from 0 to z. It implies the probability of occurrence of value less than or equal to 2 while sampling from a normal distribution with mean0 and standard deviation 1 is:0.977. In the graph, fifty percent of values lie to the left of the mean and the other fifty percent lie to the right of the graph. CDF Value of x2 in normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 is :0.9772498680518208. The center of the curve represents the mean of the data set. p: the value(s) of the probabilities, mean: mean of Normal distribution (location parameter), sd: standard deviation of Normal distribution (scale parameter).

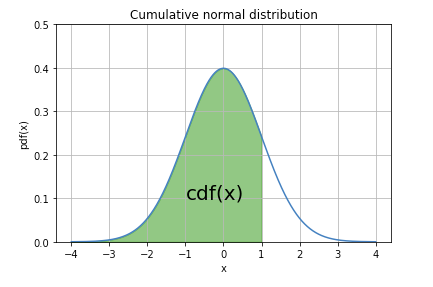
The syntax to compute the quantiles of Normal distribution using R is. p is the probability that a single observation from a normal distribution with parameters and falls in the interval (-, x. CDF of Normal Dist Normal Distribution Quantiles using qnorm() in R. Which means, on plotting a graph with the value of the variable in the horizontal axis and the count of the values in the vertical axis we get a bell shape curve. In other words, the cumulative distribution function for a random variable at x gives the probability that the random. The normal cumulative distribution function (cdf) is p F ( x, ) 1 2 x e ( t ) 2 2 2 d t, for x. if X and Y are independent, then F X Y ( x, y) F X ( x) F Y ( y).
#CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION CODE#
Code faster with the Kite plugin for your code editor, featuring Line-of-Code Completions and cloudless processing.
#CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION FREE#
The joint CDF has the same definition for continuous random variables. Kite is a free autocomplete for Python developers. Let's start off first by covering some basics.In a random collection of data from independent sources, it is generally observed that the distribution of data is normal. 5.2.2 Joint Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) We have already seen the joint CDF for discrete random variables. The cdf is not discussed in detail until section 2.4 but I feel that introducing it earlier is better. As usual, some brief coverage of the mathematics and code will be included to help drive intuition. The cumulative distribution function (CDF or cdf) of the random variable X has the following definition: F X ( t) P ( X t) The cdf is discussed in the text as well as in the notes but I wanted to point out a few things about this function. The first method using the central limit theorem, and the second method using the Box-Muller transform. Use the CDF to determine the probability that a random observation that is taken from the population will be less than or equal to a certain value.
#CDF OF A NORMAL DISTRIBUTION HOW TO#
In this post, we'll be reviewing the normal distribution and looking at how to draw samples from it using two methods. The cumulative distribution function (CDF) calculates the cumulative probability for a given x-value. It's also of great importance due to its relation to the Central Limit Theorem. Many natural phenomena can be modeled using a normal distribution. It is used to specify the distribution of. One of the most common probability distributions is the normal (or Gaussian) distribution. Cumulative Distribution Function states that the probability of the real-valued random variable X, will always take a value less than or equal to X.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
